Whitelisting in Guardian
Guardian operates in a secured framework, with the cache separated from the recursive DNS engines. It performs a continuous real-time analysis of the inbound and outbound traffic and therefore offers complete DNS Transactions Inspection (DTI).
This analysis is especially reliable if a large number of queries is cached. By default, Guardian caches all the answers to client queries. The answers not cached yet, are sent to the DNS resolver and transmitted to Guardian, that caches them and sends them back to the client. That way, Guardian has an ever-growing
number of queries to refine its analysis of the network and avoid potential threats.
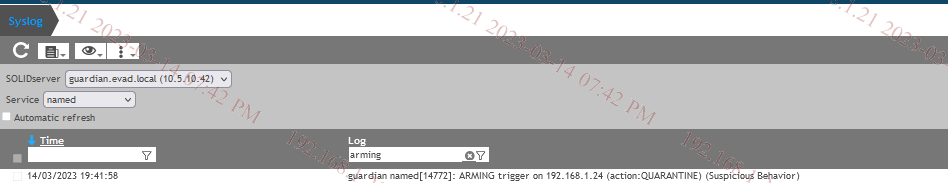
The Guradian has triggers activated based on parameters considering the cache and number of queries and other inputs. sometimes the clients are sending the queries to a DNS server which forwards to the Guardian resulting in abnormal traffic generated from one IP. so whitelisting that proxy or that DNS servers IP might be required, below is the steps to whitelist some IPs from the Guardian countermeasures.
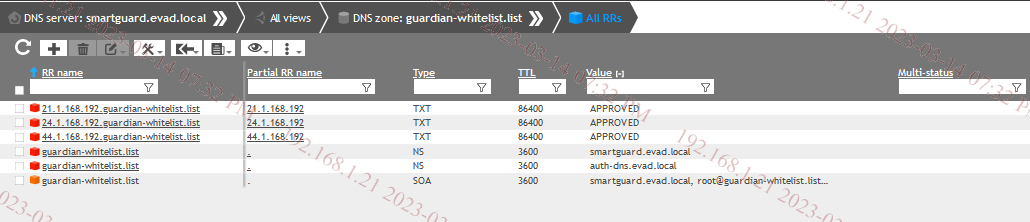
1. Create a forward zone in Guardian server; example: guardian-whitelist.list
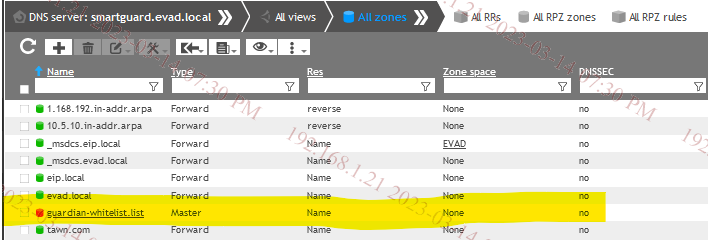
2. Add the IPs in reverse format as TXT records with APPROVED in the value.
You can whitelist the whole network by adding wildcard mask *.1.168.192.
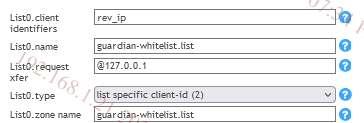
3. Edit the Guardian options to include the following:
![]()
4. Enable xfer account in Guardian services: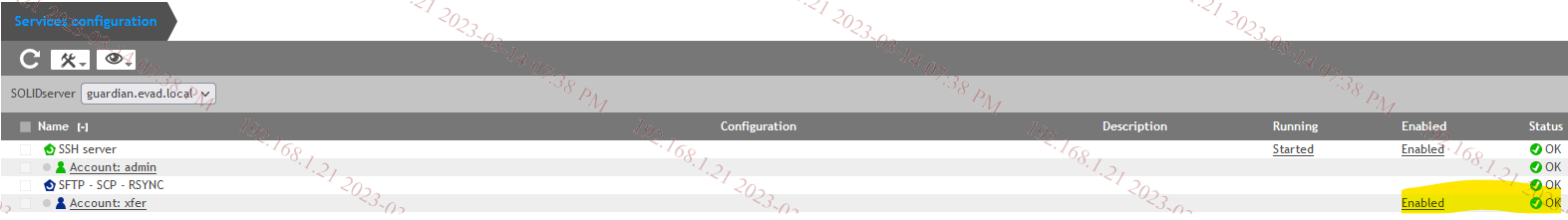
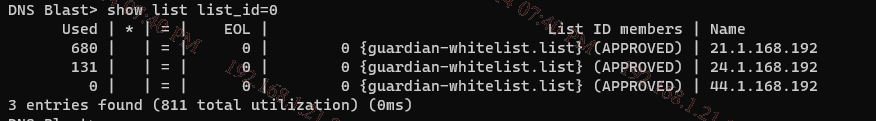
5. Confirm the list is being transferred to list0 from blastcli:
6. Execute abnormal DNS traffic like nslookup DGA domains:
The trigger will be fired but the action of quarantine will have no impact ;)